Biotechnological Medicine...

What?
Biotechnology is a branch of multidisciplinary science and technology that uses living organisms or systems to produce useful products that improve the quality of human life. New products are obtained as a result of interactions between biological sciences and technology, in fields such as biology, biochemistry, and microbiology. The active ingredients of biological medicines are peptides or proteins. Peptide or protein-like drugs are purified directly from biological environments, and living organisms are produced by chemical synthesis or using technological methods. Peptides up to 50 amino acids in size can be synthesized by chemical methods. Larger proteins can be obtained by recombinant DNA technology, or by purification from biological media.
Biotechnological studies in the field of health include gene therapy, recombinant vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, and the production of artificial organs and tissues to replace damaged or dysfunctional organs and tissues in humans. Nowadays, biotechnological studies achieve rapid development, especially in pharmaceutical production.

Production
Biotechnological medicines are produced using recombinant DNA technology. Recombinant DNA technology is a series of methods used to create recombinant DNA, the process of cloning a gene fragment and expressing protein from the gene used.
Biotechnological medicines have larger molecules compared to conventional drugs, and each has a number of inherent properties that vary to some extent. This variability can be in the type and length (glycosylation) of any sugar or carbohydrate that may have been added to the molecule by the 'shape' (folding) of the molecule. Biotechnological medicines are produced using living organisms. The production process is complex and requires advanced technology as the final product, the biological active substance, must be purified from thousands of other molecules in the living cell or organism.
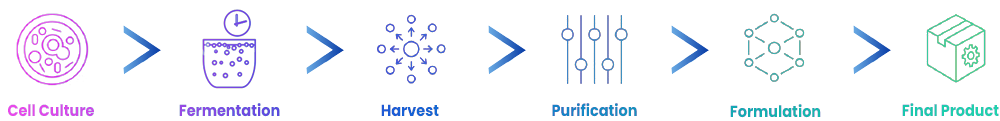

Comparison with Conventional Drugs
While conventional drugs are products of chemical synthesis, biotechnological medicines are biological products obtained from living cells.
Chemical Medicines:
- They are small molecules.
- They are simple structures.
- They are resistant to serum proteases.
- There are no stability problems.
- They have well-defined modifications.
- It is obtained via chemical synthesis.
- There are few critical processing steps during production.
- It is easy to characterize completely.
- It is not immunogenic.
Biological Medicines:
- They are small and large complex molecules.
- They are complex structures.
- It is sensitive to serum proteases.
- There are stability problems.
- Modification options are numerous.
- It is obtained from living cells.
- There are many critical processing steps during production.
- It is impossible to fully characterize.
- It is generally immunogenic.
